Methodological notes on the publication ’Financial assets and liabilities of the households sector’
The publication ‘Financial assets and liabilities of the households sector’ provides information on the households sector’s balances and transactions in the context of financial assets and liabilities. It’s a part of the sectoral balances and financial accounts of the System of National Accounts of the Russian Federation for the households sector formed by the Bank of Russia in accordance with Clause 16.1 of Article 4 of Federal Law No.
The data on financial assets and liabilities of the households sector are published on a quarterly and monthly basis in accordance with the Official Statistics Release Calendar. The data on financial assets and liabilities of the households sector on a monthly basis contain information on selected most important financial instruments.
Financial assets and liabilities of the households sector’ presents the data broken down by different financial instruments what make it possible to analyze household consumption and saving behavior, household preferences regarding investing in financial instruments, the dynamics and structure of households’ savings. Information on household savings helps to improve the consistency of data on household money income and spending, financial accounts, and sectoral balances of the System of National Accounts (SNA).
The data and format of the publication can be updated due to changes in the reporting data, emergence of new data sources, and methodological changes.
1. Methodological principles for compiling the data on financial assets and liabilities of the households sector
The System of National Accounts 20081 (SNA 2008) is the methodological basis for the compiling financial assets and liabilities of the households sector.
According to the SNA 2008, the balances of financial assets and liabilities show stocks of financial assets and liabilities at a certain point in time. Asset value at a certain point in time changes each time in accordance with a transaction, price change, or any other change influencing the amounts of assets and liabilities.
The balances of financial assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currency are converted to the national currency at the exchange rate on the last business day of the reporting period.
Transactions are economic flows between institutional units that occur by mutual agreement. Transactions with financial assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currency are converted into national currency at the average exchange rate in the period of transactions. As a rule, transactions are valued at the market price. In the case of lack of information, indirect methods are used to value transactions.
The household transactions with non-traded shares and other non-resident equity and investment fund shares are measured in accordance with methodological approaches of the sixth edition of the Balance of Payments and International Investment Position Manual (BPM6)2 and are presented in the balance of payments of the Russian Federation.
In the absence of data on transactions and the balances of financial assets and liabilities of the households sector, these indicators determined by the residual method based on known total amounts across all economic sectors.
Definition of the households sector corresponds to Appendix B ‘Classification of institutional sectors of the economy’ of the All-Russian Classification of Forms of Incorporation OK
An institutional unit is an economic entity that is capable, in its own right, of owning assets, incurring liabilities and engaging in economic activities and in transactions with other entities (SNA 2008: 4.2). Institutional units grouped into sectors and subsectors.
The households sector includes institutional units consisting of one individual or a group of individuals, including individual entrepreneurs.
Methodology of formation for financial assets and liabilities related to the households sector might be a subject to change due to development of methods and approaches to estimate given indicators within the process of harmonisation of SNA.
2. Classification of financial instruments
The classification of financial instruments used for compilation financial assets and liabilities of households developed in accordance with the SNA 2008.
Currency – notes and coins issued by central banks. Household assets in form of cash consist of national currency that may only be the liability of the central bank and foreign currency that may only be the liability of the rest of the world. Households operations with foreign currency include buying/selling foreign currency from residents and non-residents.
Transferable deposits – household funds in settlement, current and other demand accounts (including banks’ card payment accounts) in rubles opened with the operating credit institutions.
Other deposits – household funds in time deposit accounts and other funds raised for the term in rubles, all types of foreign currency deposits, precious metal accounts, as well as accrued interest on deposit opened with operating credit institutions.
Deposits with non-resident banks – household funds in settlement, current and other demand accounts (including banks’ card payment accounts), time deposit accounts opened with non-resident banks in foreign currency.
Broker accounts of households – household funds in broker accounts of professional securities market participants (credit and non-bank financial institutions) intended to record customer funds and settlements with customers and third parties in broker operations, which are transactions of professional securities market participants with securities and precious metals, and (or) foreign currency, as well as derivative agreements, on the account of and on behalf of customers under instruction or commission agreements.
Debt securities – bonds, bills, savings certificates, certificates of deposit, depository receipts for bonds and other debt securities. Debt securities give their holders the right to receive contractually determined payments on a specified date. Transactions in debt securities include issuance, redemption, purchase and sale.
Loans – all loans including overdraft facilities, except receivables/payables. Loans in household liabilities include loans as well as credit claims acquired by credit institutions: housing mortgage loans, car loans, consumer loans, other loans and claims on accrued interest, housing mortgage loans sold to mortgage agents (including repayment), consumer loans sold to specialised financial companies, as well as loans received from microfinance organisations.
Equity and investment fund shares – shares, including investment funds’ equity, depositary receipts for shares, investment units of unit investment funds and other equity. Listed shares are admitted for trading and included in Quotation lists (Level One and Level Two) on the Moscow Exchange. Unlisted residents shares include shares admitted to organised trading and included in quotation lists (third level) on the Moscow Exchange, as well as shares not traded on organised trading venues. Listed non-resident shares are shares with a market quotation for the three months preceding the reporting date. Information on the estimated value of equity securities issued in the unlisted shares is compiled in accordance with international standards: the value of unlisted shares is assessed based on companies equity. Shares and other equity represent the owner’s funds in the institutional unit. Consistent with BPM6, other holdings of non-residents’ equity include other capital investments (free aid, maintenance, consulting, personnel training, etc.), as well as cross-border investment in real estate considered as direct equity investment in a notional unit.
Insurance, pension and standardised guarantee schemes – life and non-life insurance reserves, as well as pension entitlements, entitlements to non-pension benefits, as well as data on long-term savings agreements.
Other accounts receivables/payable – debt related to purchase and sale of securities, dividend payments, rent, wages, tax payments and payments for utility services, as well as other receivables/payable debt.
Escrow accounts of households - funds in individuals accounts opened for settlements operations under equity construction agreements as well as under real estate purchase and sale transactions in accordance with the law of the Russian Federation
3. Methodological principles for seasonal adjustment of transactions
Transactions are derived from balance data in accordance with SNA 2008 by taking the difference between balance data for each instrument at the reporting date and at the beginning of the period, after adjusting for revaluation and other changes of the volume of assets:
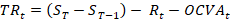
where 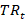 – transaction in period
– transaction in period 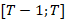 ,
, 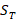 – balance as of date T,
– balance as of date T, 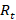 – exchange rate and market revaluation of financial assets in period
– exchange rate and market revaluation of financial assets in period 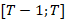 ,
, 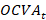 – other changes of the volume of assets in period
– other changes of the volume of assets in period 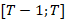 .
.
Seasonal adjustment of financial assets and liabilities of the households sector is done in line with ESS Guidelines on seasonal adjustment (Eurostat, 2024, 2018)3 and Monetary and Financial Statistics Manual and Compilation Guide (IMF, 2016)4 using X-13 ARIMA/SEATS (US Census Bureau). Use of that tool helped to diminish the risk of oversmoothing of time series and account for the economic situation in the country. The following approach is applied for seasonal adjustment of transactions:
Step 1. Seasonal adjustment of cumulated other changes.
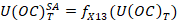
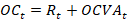
where 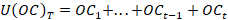 – cumulated other changes, including exchange rate and market price revaluation ,other volume changes of assets as of date T. In cases where seasonal adjustment applied to time series in the national currency, then
– cumulated other changes, including exchange rate and market price revaluation ,other volume changes of assets as of date T. In cases where seasonal adjustment applied to time series in the national currency, then 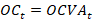 . In order to exclude non-transaction flow from stocks series, other changes are considered as cumulated totals.
. In order to exclude non-transaction flow from stocks series, other changes are considered as cumulated totals.
Step 2. Seasonal adjustment of stocks series excluding cumulated other changes.
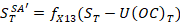
where 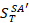 – seasonally adjusted balance excluding cumulated other changes as of date T.
– seasonally adjusted balance excluding cumulated other changes as of date T.
Step 3. Definition of a seasonally adjusted transaction.
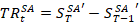
где 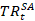 – seasonally adjusted transaction.
– seasonally adjusted transaction.
1 System of National Accounts 2008 (European Commission, United Nations, Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, International Monetary Fund, World Bank).
2 Balance of Payments and International Investment Position Manual, Sixth Edition (BPM6), International Monetary Fund, 2009.
3 European Statistical System (ESS) Guidelines on Seasonal Adjustment/ Eurostat, Manuals and guidelines/ Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union, 2024. Handbook on Seasonal Adjustment/Eurostat, 2018.
4 Monetary and Financial Statistics Manual and Compilation Guide/Washington, D.C.: International Monetary Fund, 2016.
